
Microfluidic NMR (微流控核磁)
分子组装机理研究离不开合适的表征方法,而分子组装涉及多级次、多位点、弱键非共价相互作用、协同和反馈,这些特点要求表征方法具有高能量分辨、空间分辨和时间分辨。核磁共振技术本身已具备高能量分辨和空间分辨,被广泛用于表征复杂组装体结构和动态过程,但核磁灵敏度低,导致其时间分辨率差,不适合监测组装中间过程。我们与英国南安普顿大学合作发展了微流控核磁技术,将核磁共振技术的时间分辨率提升至秒级(一维谱和二维谱);组装基元在微流控芯片内原位混合并组装,最快可采集组装开始1秒时的核磁谱。微流控核磁技术填补了核磁技术低时间分辨的短板,使其更好地用于表征分子组装中间过程,揭示组装机理。
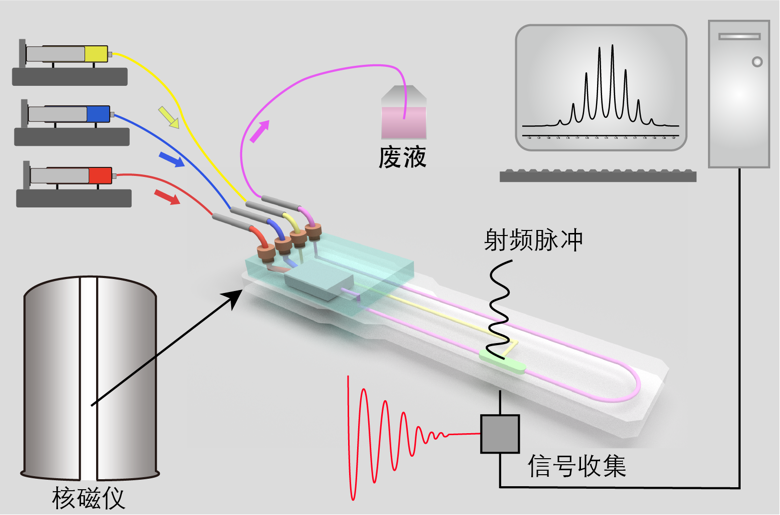
Revealing the mechanism of molecular assembly require proper characterization methods. Because molecular assembly involves hierarchical, multi-sites, weak non-covalent interaction with synergy and feedbacks, characterization methods need to have high energy, spatial, and time resolution. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) have high resolution in energy and spatial, but due to its poor sensitivity, the time resolution of NMR is poor, which makes it difficult to monitor assembly process. In collaboration with University of Southampton, we developed microfluidic NMR, bring the time resolution of NMR up to 1 s (both 1D and 2D NMR spectra). Moreover, the building blocks are mixed and assembled inside the microfluidic chip, enabling acquisition of NMR spectra after the assembly started in 1 s. Microfluidic NMR filled the shortcomings of NMR, making it suitable for monitoring process of molecular assembly and unraveling mechanism.
Complex Assembly System © Copyright 2020
